TRANSFER / OUTREACH Strategic orientations
Transfer and innovation generally take a classical economic meaning epitomized by patents, but this hardly covers
what happens in the field of biodiversity (proposing solutions to threatened biodiversity is one objective of Cemeb),
where innovation is certainly useful. However, transfer should more broadly include socio-economic players involved in
biodiversity management and outreach - an area sub-optimally connected to research and under-funded compared to
classical innovation. This defines Cemeb view that was presented at InEE CNRS assizes (2017), and drives its transfer
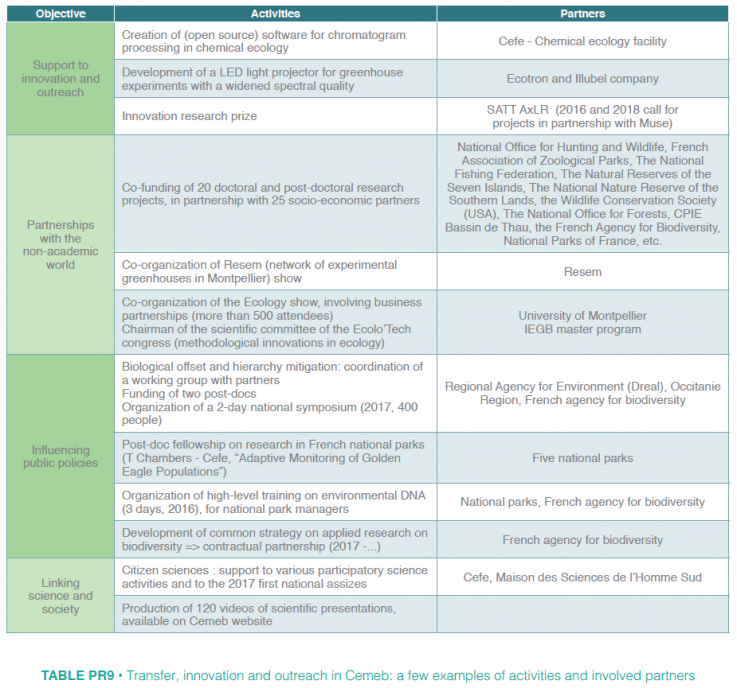
activities along four lines (Table PR9):
- Stimulating innovation : in collaboration with the SATT AxLR (a state agency funding innovation), Cemeb systematically evaluated whether research projects from its community (especially all those submitted to Cemeb calls for projects) canlead to innovation and therefore to further discussion / activities with project leaders. Cemeb also launched several calls for projects (Table PR9), the last of which in collaboration with the I-site Muse and AxLR (on-going);
- Stimulating partnerships with the non-academic world: Cemeb actively developed partnerships with ca. 98 partners from both the public (non-academic) and private sectors in order to speed up the transfer of research results. The most visible aspect was (co)funding PhD and post-doctoral projects co-supervised by Cemeb researchers and non-academic players, such as engineering companies and National parks, on a variey of topics (see portraits of F. Holon and A.-C.Vaissières in this report), three of which obtained a non-academic positions. Cemeb also co-organized events gathering researchers, biodiversity managers, and the private sector. The largest is the yearly “Salon de l’écologie” (Table PR9);
- Influencing public policies on environmental issues: Cemeb develops a strong partnership (the only Labex to do so) with the French Agency for Biodiversity (Ministry for Ecological and Solidary Transition) developing research projects on biodiversity management through PhD, post-doctoral and engineer hiring to sustain the link between fundamental research and practical solutions to biodiversity issues (Table PR9). Cemeb is strategically involved in developing the ‘biodiversity offset and mitigation’ hierarchy from both an ecological and economical point of view with regional and national partners (Table PR9).
- Linking science and society: Cemeb sustains / organizes outreach and participatory and citizen sciences to reinforce this link on critical issues at the heart of Cemeb project (e.g., the evolutionary theory, the biodiversity crisis) through project and meeting funding (see an interesting example in Table PR9) and video production. Cemeb also sustains focused outreach activity (e.g., through the Evolution2018 congress).
FOCUS : Anne-Charlotte Vaissiere

FOCUS : DIVERSITY OFFSET AND MITIGATION HIERARCHY COLLOQUIA - MARCH 2017
 Gathering over 200 attendees, from regional and national scales, and over 50 speakers, this colloquia has been organised in two days :
Gathering over 200 attendees, from regional and national scales, and over 50 speakers, this colloquia has been organised in two days :
March 30, 2017 : Regional seminar featuring interactions between research and developpers of urban infrastructures (Government, Regions, collectivities, privates entreprises).
March 31, 2017: Scientific day (ecology, ethics, phylosophye, socio-economy, geography, law).
More infos and videos (French) >
EXAMPLES OF TRANSFER & INNOVATION ACTIONS